Breath retention practices are not appropriate for public yoga classes. Regardless of what you learned in your yoga teacher training, what you have experienced while being a student, or even what you have taught in your classes for years.

Those who have studied in a class or teacher training setting with me will have already heard this from me many times and it deserves repeating because it’s essential for the health, vitality and yoga journey of all those attending public yoga classes.
There are many reasons why breath retention practices do not belong in public yoga classes ranging from medical red flags to impeding your student’s ability to gain equanimity along their spiritual journey. Breath retention is going to amplify whatever is in the body, mind and energy. If a student is experiencing any sort of imbalance, breath retention practices will exacerbate the imbalance.
There is a long list of prerequisites for breath retention practices here. The student needs to be appropriately prepared for these intensive practices in order for them to be beneficial and not cause harm. This is why, for countless generations, these powerful breath retention practices have only been taught under the care and strict observation of master teacher to devoted student. This approach to teaching grants the teacher in-depth knowledge of the student, their practice, their health on all levels and the teacher is able to directly monitor the student so they can adapt/discontinue the practices when necessary.
However, in the average public yoga class, teachers have nowhere near enough knowledge on every single student’s physical, emotional and mental states to determine if advanced breath practices are appropriate – sometimes we don’t even know the student by name.
The American Heart Association acknowledges that mid-cycle rest (a pause in the breath at any point in the cycle) has been associated with increased incidence of arrhythmia, heart failure, stroke and high blood pressure. Sleep apnea (a condition in which the breath stops mid-cycle during sleep) is a common example of mid-cycle rest in the breath cycle and according to the AHA is experienced by 1 in 5 folks.
“When the air flow stops, the body releases stress hormones, which over time can lead to heart disease — the leading cause of death in the United States — stroke and high blood pressure. It also can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, liver problems and metabolic syndrome.” – https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/sleep-disorders/sleep-apnea-and-heart-disease-stroke
Why teach our yoga students a practice which will only reinforce and deepen a pattern which is known to cause major health concerns?
Without being properly prepared and monitored, breath retention practices can also trigger trauma, PTSD and re-traumatized students recovering from traumatic events. In addition to all of these risks, the student’s spiritual journey can also be compromised with the use of breath retention practices.
When studying the yoga sūtra, we learn that all humans share patterns of suffering and mental fluctuations. While all of our individual sufferings are distinct and valid – as a whole, our sufferings can be categorized into 5 broad categories.
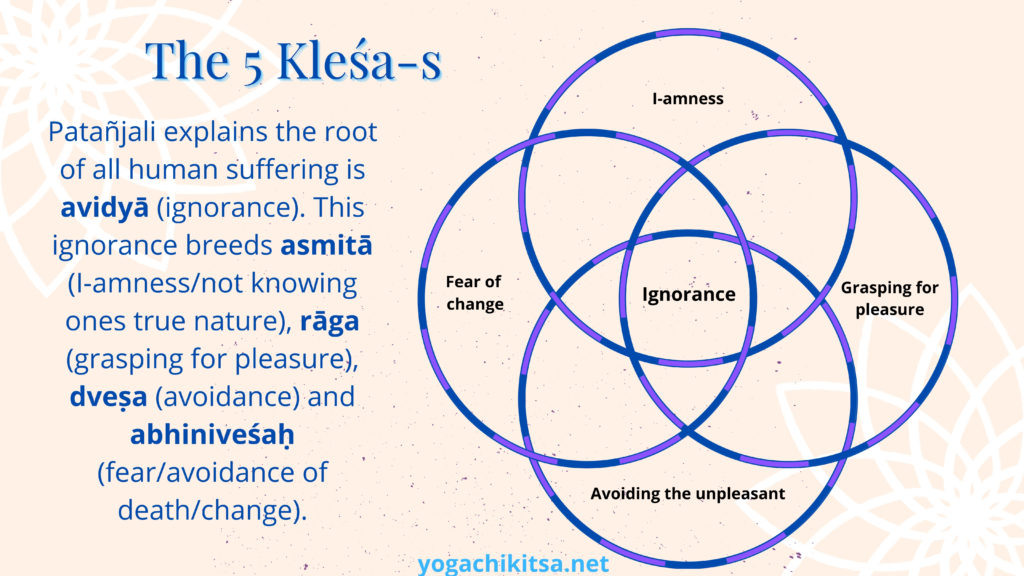
Patañjali explains the root of all suffering is avidyā (ignorance). This ignorance breeds asmitā (not knowing ones true nature), rāga (attraction), dveṣa (avoidance) and abhiniveśaḥ (avoidance of death/change). These afflictions can certainly be reduced with appropriate practice and can be fueled with practices that are not fitting for the student.
If we teach students breath retention practices before they have done the necessary work of weakening the kleśa-s, we will unknowingly contribute to them strengthening these patterns of suffering. Students will find themselves stuck in a web of these afflictions, bouncing back and forth between different patterns and experiences of suffering. The student will then not able to genuinely settle into an experience of samādhi (mental absorption on an object, task, etc.).

Instead of teaching breath retention practices in public yoga classes, focus on helping your students find balance in their breath from inhale to exhale – without any pauses and reinforce this pattern of even breath throughout class. This approach to breathing has been proven to increase cardiovascular health, balance the nervous system, increase heart rate variability and create a foundation for a meditative experience. This will also strengthen the student’s ability to transition from sympathetic nervous system (fight/flight) to parasympathetic nervous system (rest/digest) with greater ease and an easeful transition between sympathetic and parasympathetic is a foundation for changing reactionary patterns and weakening the influence of the kleśa-s.
If we want to support yoga being a practice for any body, we MUST create an environment in which everyone can receive the benefits of yoga, this includes education on what practices are supportive for everyone and clear knowledge of practices that are advanced and not appropriate for the average Saturday morning class at a local studio.

eBook – The Sound The Heart Sings, a journey inward with sacred sanskrit sounds


